You've already started learning about living things in Grade 1 and Grade 2. Now that you're in Grade 3, let’s explore even more cool facts about plants and animals!
What Are Living Things?
Plants and animals are living things. Another word for living things is organisms. All living things share some special features:
1. Living Things Grow!
All living things use energy to grow and change as they get older. For example, a tiny sunflower seed grows into a small green plant, and then into a tall flower with a strong stem.
2. Living Things Respond to the World Around Them!
Living things notice and react to what's happening around them.
When you're cold, your body shivers to warm you up.
When you're hot, you sweat to cool down.
A plant in the shade will bend toward the sunlight.
A bird might fly away if it sees a cat nearby.
In fall, some trees drop their leaves to get ready for winter.
3. Living Things Reproduce:
To reproduce means to make more living things like themselves.
An apple tree makes seeds that can grow into new apple trees.
A chicken lays eggs, and baby chicks hatch from them.
What About Nonliving Things?
Nonliving things are all around us too!
Things like rocks, soil, and water come from nature but are not alive.
Things like cars, roads, and buildings are made by people.
Nonliving things do not grow, do not respond, and do not reproduce.
Living Things and Their Environment:
Living things need certain things from their environment to stay alive.
The environment is everything around a living thing, including both living and nonliving things.
All living things need Food, Water, Air and Space.
What Are Living Things Made Of?
All living things are made of tiny parts called cells. Cells are so small you can't see them with just your eyes, you need a special tool called a microscope to see them! Some living things, like bacteria, are made of only one cell!

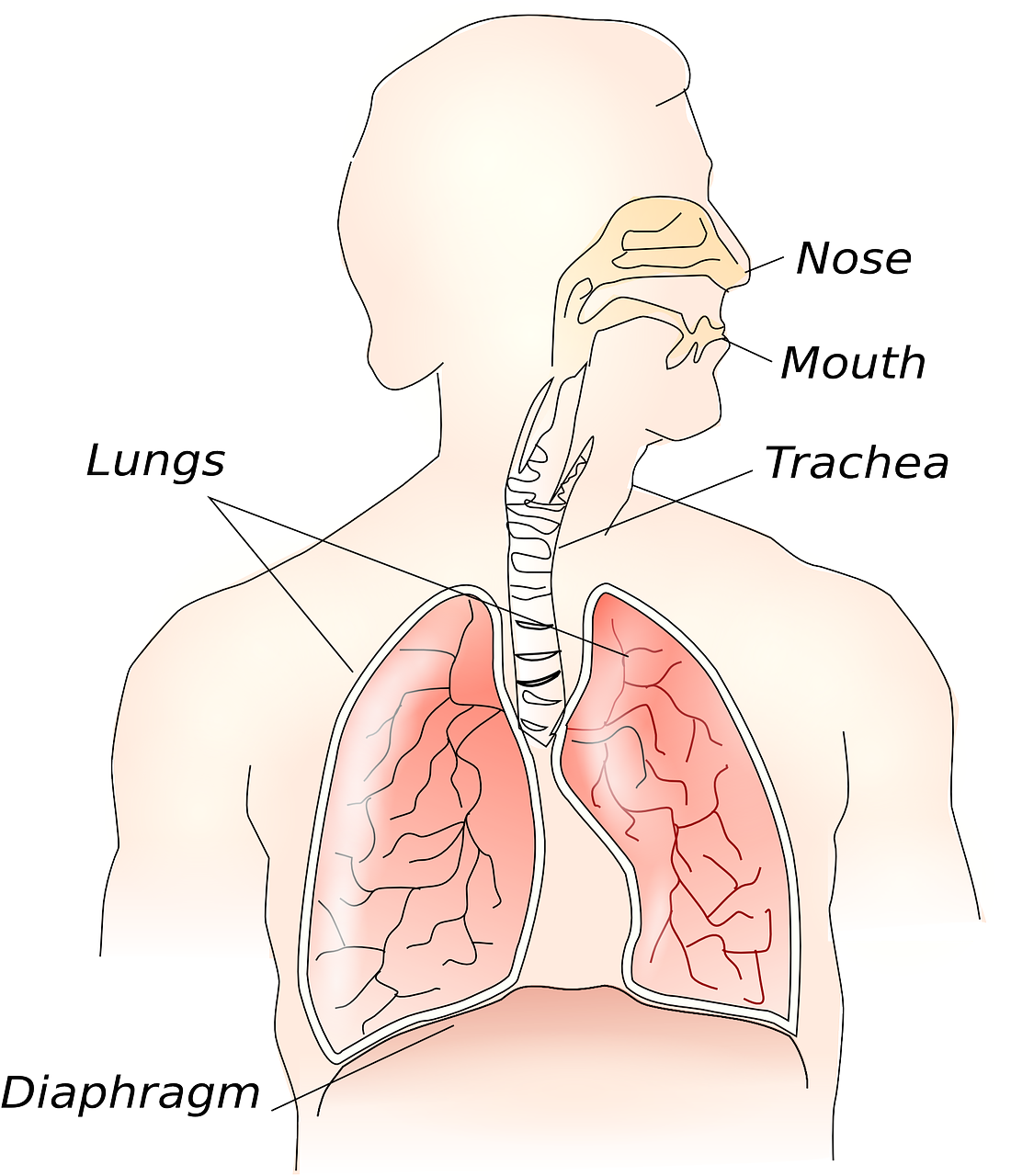
Oxygen: Animals breathe to get oxygen. Many animals breathe with lungs. Lungs are structures that take in oxygen from the air. Fish get oxygen using gills. Gills are structures that take in oxygen from the water. Some animals can breathe without lungs or gills. Worms and salamanders, for example, take in oxygen through their skin.
Food and Water: Animals use various structures to obtain food and water. Birds have specialized beaks to catch worms. lions can run fast and have strong jaws to grasp their prey. dogs have shapr canine teeth to tear through meat. Cows have hard gums and lips to prevent them from being injured by the shapr blades of grasses.
Moving: Animals move in search of food, water and shelter, and away from danger. Movement can be done in various ways. Most animals use legs to move. Some have the ability to fly. Other animals, such as snakes, do not have legs and they slither on the ground.
Staying safe: Animals stay safe from danger and from extreme weather events. Some animals dig the ground and shelter there. Lizards stay under rocks. some birds build nests. Tortoises and snails move around with their shells as protection.
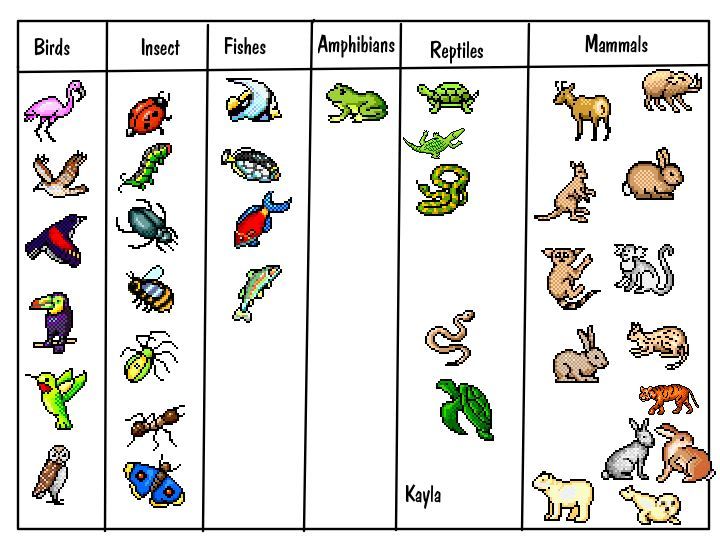
Classifying animals to form smaller groups makes it easier for scientists to study them. One way scientists classify animals is by their structures.
Animals with backbones are called vertebrates. Tigers, dogs, eagles, people, goldfish etc are vertebrates.
Animals that do not have a backbone are called invertebrates. Insects, spiders, worms, snails etc are some examples of invertebrates.
Some invertebrates, such as insects, lobsters etc have a hard shell on the outside called an Exoskeleton.
Birds: Birds are a kind of animals that have a beak, feathers, two wings and two legs. they are built to fly, though not all of them do a good job at it.
Reptiles: Reptiles are vertebrates with a rough scaly skin. Crocodiles, snakes, turtles are some examples. Some reptiles live on land while others live in water. All reptiles breath through their lungs, so they lift their heads above water to breath.
Amphibians: are a group of animals that spend a part of their lives in water and part on land. Frogs, toads and salamanders are examples. Most start as eggs which hatch into a fish-like stage that breaths through gills. As they get older, they grow legs and lungs and begin to live on land.
Fish: fish are vertebrates (they have a backbone). They spend their whole life in water and obtain air (oxygen) through gills. Most are covered in scales on their skin and their skin is slimy.
Mammals: mammals are a large group of diverse animals. Mammals are characterized by the presence of mammary glands that produce milk for feeding their 'babies'. Mammals have skin covered in hair or fur. All mammals breath using lungs. Some, such as dolphins and whales, live in water and rise to the surface to breath.
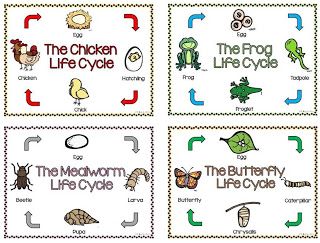
Different types of animals change in different ways. Some animals are born looking like their parents. Others are not. These animals might change shape or color as they grow. They may even grow new structures. The way an animal changes with age is part of its life cycle.
Some animals change shape through a process called metamorphosis. Amphibians and most insects go through metamorphosis. Their life cycle begins with an egg. Eggs contain food that young animals need. Most have a shell that protects the animal.
Reptiles, fish, and birds have similar life cycles. Most of these animals lay eggs. Reptiles lay their eggs on dry land. Fish lay their eggs in water. Birds often build nests to protect their eggs. Most birds sit on their eggs until the eggs are ready to hatch.
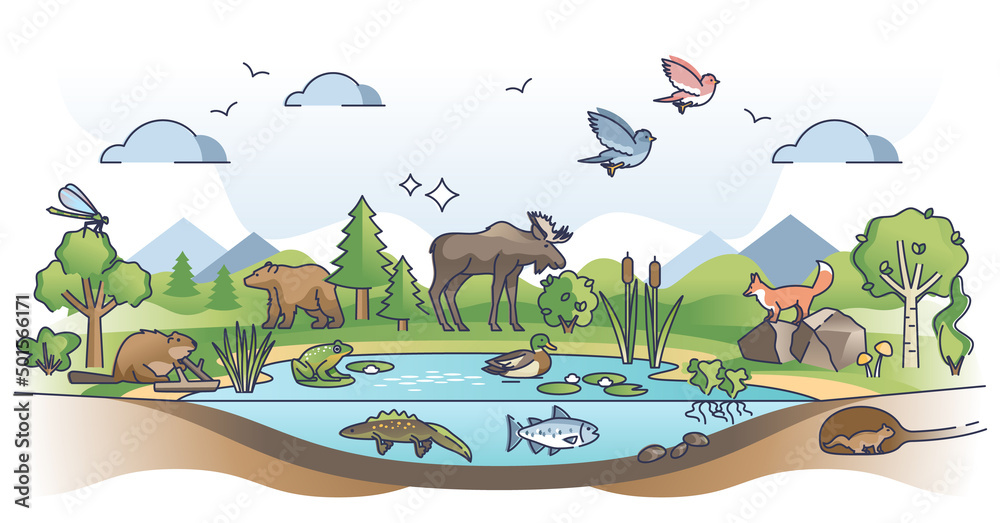
Living things depend on each other. They also depend on nonliving things like sunlight. Living and nonliving things that interact in an environment make up an ecosystem. An ecosystem may be a pond, a swamp, or a field, maybe large or small.
Different organisms live in different parts of an ecosystem. Fish live in the water, so the water is the fish's habitat.
A food chain shows how energy passes from one organism to another in an ecosystem. When a buffalo feeds on grass, they obtain energy from the grass, and when a lion feed on the buffalo, they obtain energy from the buffalo. energy flows from grass to buffalo to lion.
The first organism in a food chain is called a producer, these are organisms that make their own food. Green plants are examples of producers. Most producers use energy from the Sun to make their own food. This means that the energy in most food chains starts with the Sun.
A consumer is the organism that eats other organisms. All animals are consumers. A food chain may have many consumers.
Organisms that eat mostly plants are herbivores. Some animals, such as herons, eat mostly other animals. These organisms are carnivores. Animals that eat both plants and animals are omnivores.
Predators hunt other organisms for food. The organisms they hunt are prey.
A decomposer is an organism that breaks down dead plant and animal material. Decomposers put nutrients back into the soil. Some worms and bacteria are decomposers.
Since consumers can eat many types of organisms, many food chains can join to form a food web.
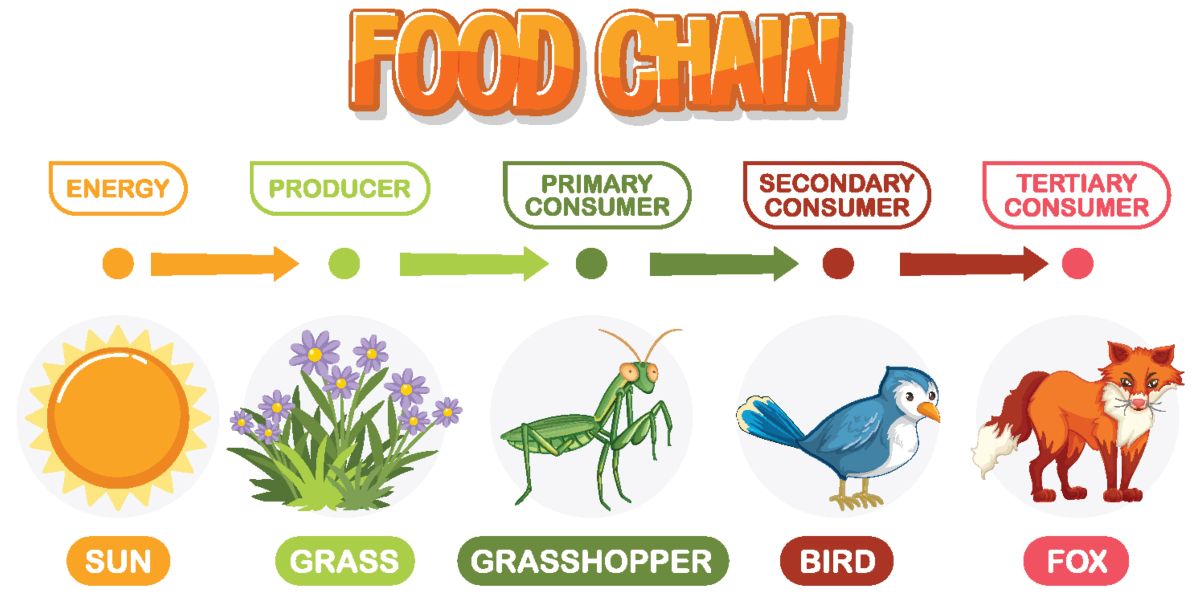
Different ecosystems have different types of soils and climate conditions. Climate is the pattern of weather in a place over a long time.
Ecosystems also differ in the types of plants and animals they have. Grasslands are covered in grass while forests are filled with trees. Oceans are filled with fish that can live in salt water. Ponds are filled with fish that can live in fresh water.
A desert is an ecosystem that has a dry climate with low rainfall of less than 25cm per year. Deserts usually have hot days but temperatures reduce drastically at night. The soil in the desert is mostly sand, with very little orgnaic matter.
A forest is an ecosystem that has many trees.
An ocean is a large body of salt water. Earth has five oceans, which are all connected. These are the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic, and Southern Oceans. The Pacific Ocean is the largest. It covers about one third of the planet. Billions of living things are found in Earth’s oceans.
A wetland is an ecosystem where water covers the soil for most of the year. Wetlands are often found along the edges of rivers, lakes, ponds, and oceans. They may have fresh or salt water.


An adaptation is a structure or behavior that helps an organism survive in its environment.
Some adaptations help living things stay safe. For example, some animals hide from enemies by blending into their. Camouflage can also help animals sneak up on their prey.
Many desert animals, such as rattlesnakes and coyotes, are nocturnal. This means they are active at night. They sleep during the day. They come out at night when the desert is cooler.
Jackrabbits have large ears that help them to stay cool as warm blood flows through the ears and heat is lost.
Some trees lose their leaves in fall as the temperature drops. This adaptation helps trees save energy.
Some forest animals blend in by looking like other, very different organisms. This adaptation is called mimicry. Mimicry is when one living thing imitates another in color or shape.
Animals like the dormouse survive by hibernating. Hibernate means to go into a deep sleep. While hibernating, animals use less energy and do not need to eat.
Migration: Animals may migrate when their environment gets too cold or when food or water is hard to find.


Every living thing changes its environment as it seeks to meet its needs to survive. A plant takes water from the soil as it grows. In this case, water is an example of a resource. We can define a resource as something that helps an organism to survive. Food, water, air, space, sunlight, shelter are examples of resources needed by living organisms.
Resources tend to be limited in availability. The ground only has enough water to support a certain volume of plants and animals. This results in the living things competing for the resources. Competition for resources means the living things that are 'stronger' and able to survive better in the environment will survive, and the weaker organisms will not be able to access the resources they need, so they will not survive.
Land itself is a reource that is also limited (scarce). As the population of people in the world increases, they compete with other living organisms for the same resources. This has resulted in people cutting down forests so as to build homes, or changing agricultural farms into malls.
People can help protect their environments. One thing people can do is practice the 3 Rs—reduce, reuse, and recycle. To reduce means to use less of something. To reuse means to use something again. To recycle means to turn old things into new things. When you practice the 3 Rs, you produce less trash and cut down on pollution.

Two years ago, in 2020, the world experienced the COVID19 outbreak and the pandemic that followed and changed people's lifestyle a great deal. Natural disasters such as floods and droughts, and diseases (such as Covid19) can change the environment directly or indirectly. Widfires also cause extensive changes to the environment.
Organisms respond to changes in the environment. Sometimes organisms develop adaptations that enable them to survive in the new environment. Sometimes they migrate to other regions where they can survive. And in some unfortunate cases, living organisms die when the environment changes. For example, widl fires may rsult in the death of many trees in a forest.
Let us define two more words: A population is the number of all the members of one kind of organism in an ecosystem. For example if you count the number of coyotes in Alberta, Canada. You need to define the region you are refering to. A community is all the populations in an ecosystem. Notice that a community is made up of individuals from many groups, not the same group. So a community will include the number of coyotes, wolves, foxes, deers, bears plants etc.
An organism is endangered when there are only a few living members of its kind left.


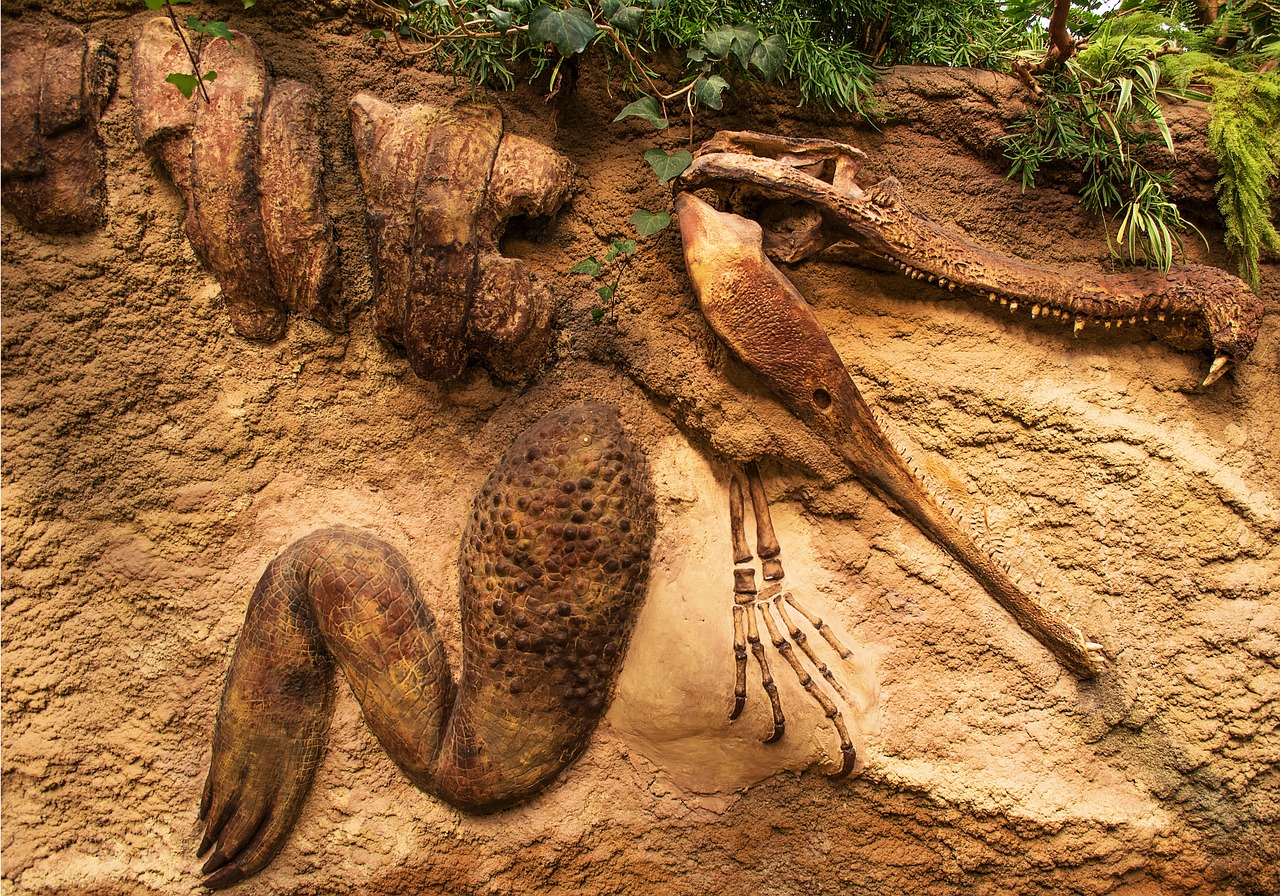
Millions of years ago, dinosaurs may have been roaming through the land that is now your town! All that is left of dinosaurs today is their fossils. Fossils are the remains of organisms that lived long ago. Many scientists think that dinosaurs became extinct after a meteor hit Earth a long time ago. A living thing is extinct when there are no more of its kind alive.
Some plants and animals are becoming extinct even today. Some scientists think that up to 100 kinds of organisms become extinct each day! In 1996 a type of mammal called the red gazelle became extinct. It was hunted too often by humans.
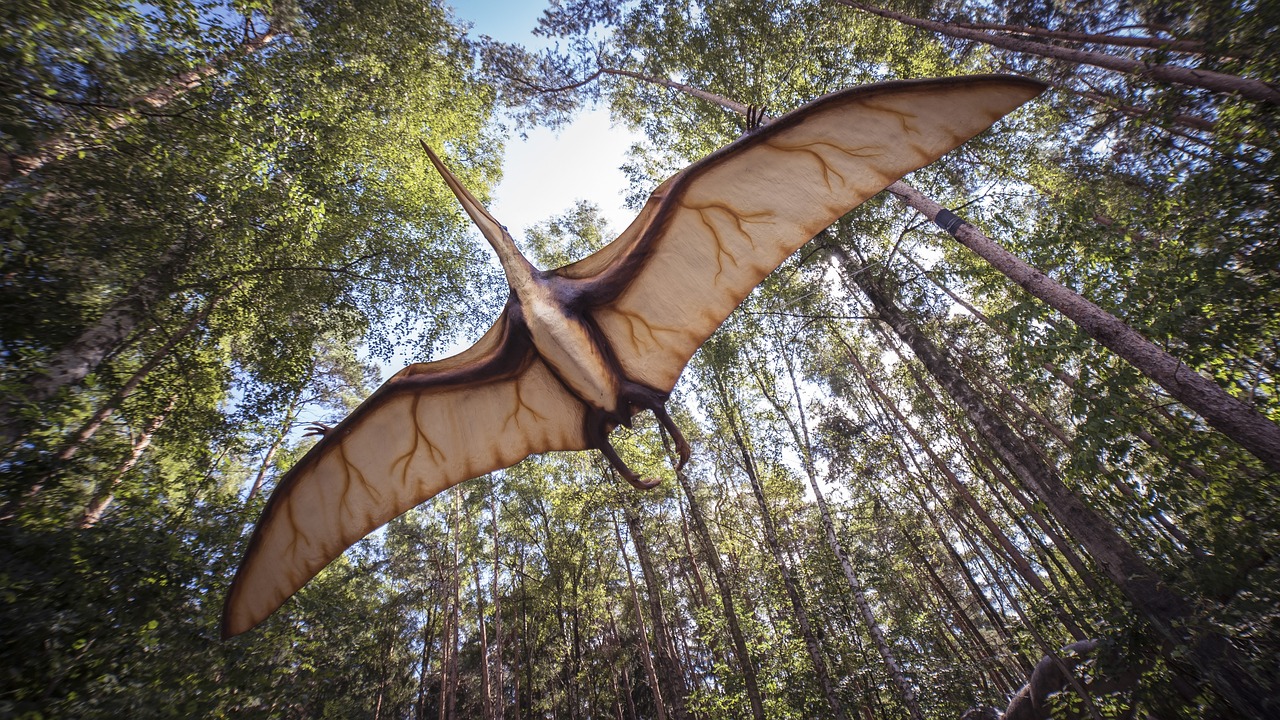
Many organisms living today look similar to those that lived long ago. Some modern birds resemble ancient reptiles. Eagles look very similar to flying reptiles called pterodactyls. Pterodactyls had long wingspans and large beaks. Scientists think pterodactyls used their beaks and claws to catch fish just like eagles.


An Ocean is a large body of salt water.
A continent a large area of land.
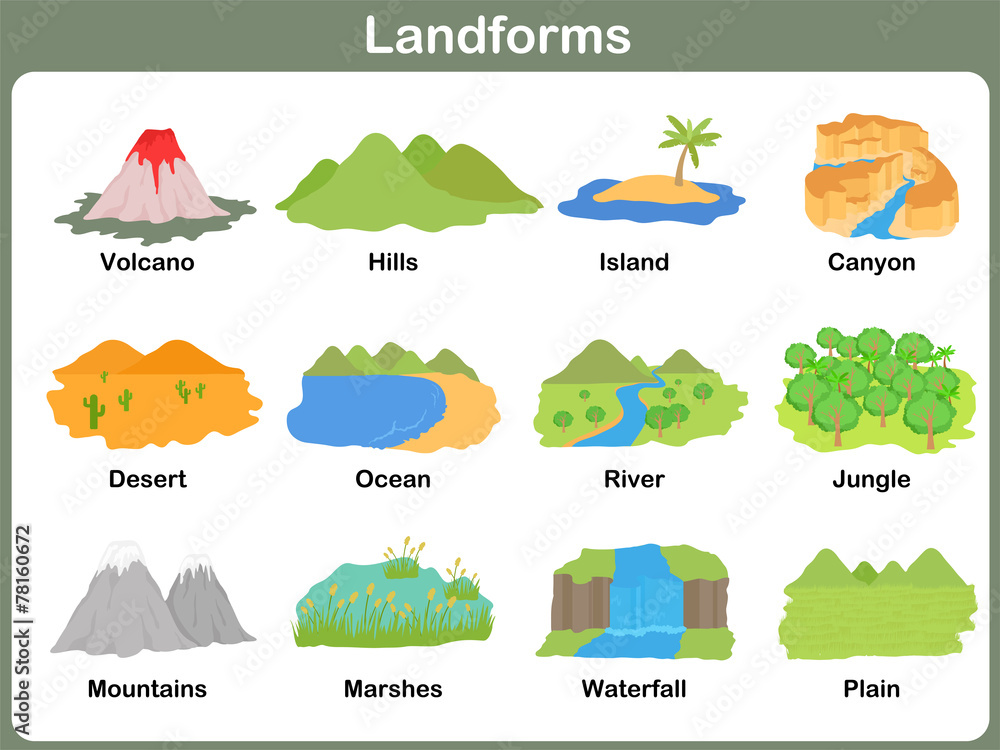
A Landform is a feature of land on the earth's surface.
Weathering is the breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces.
Erosion is the movement of weathered rock or soil by water or wind.
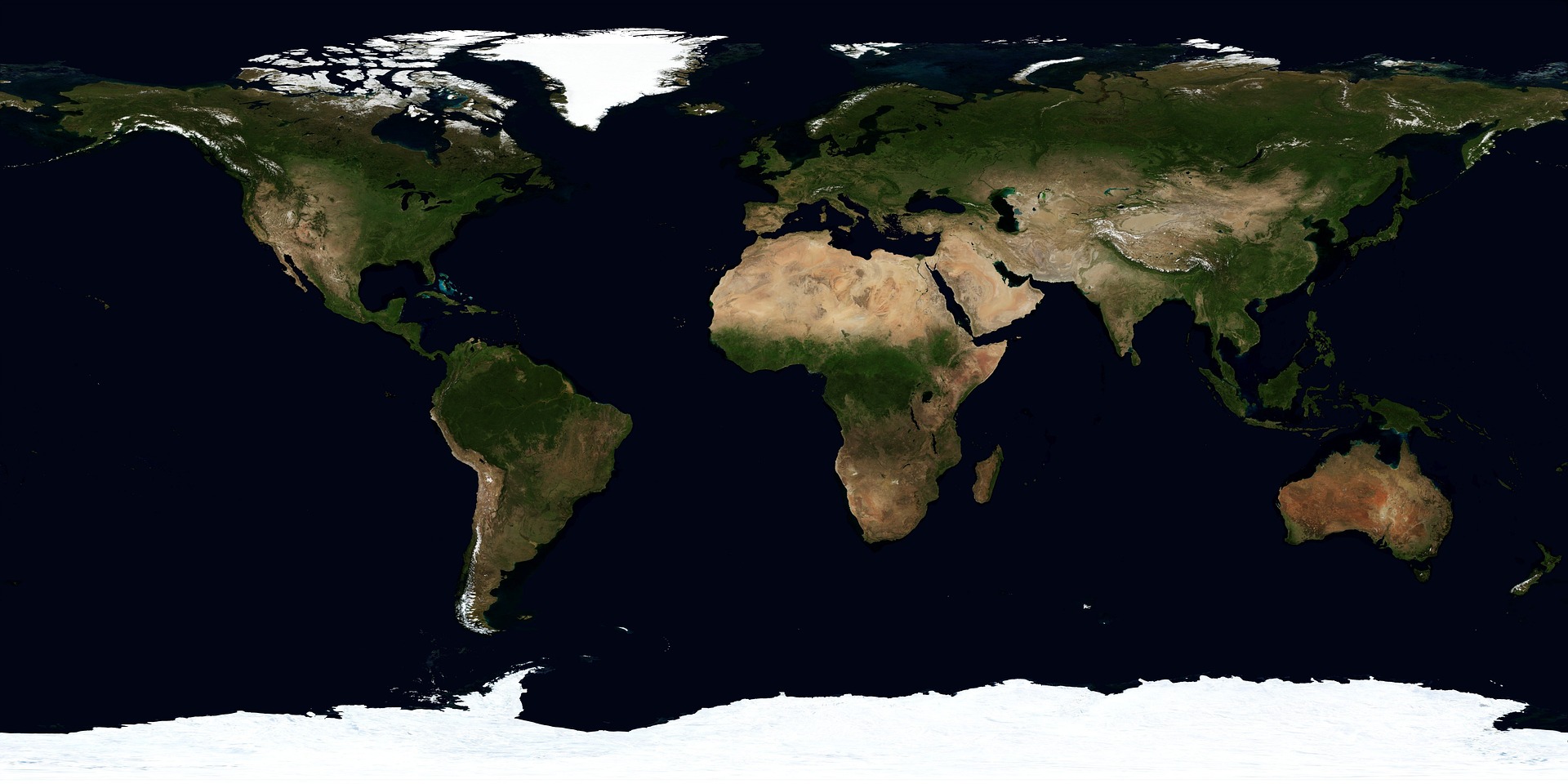
Most of the earth is covered by water. Most of this water is in oceans. Rivers, lakes, ponds, streams, glaciers etc are other types of water bodies. Oceans are made up of salt water. Lakes may be salty or fresh water. Rivers, streams and ponds are made up of fresh water.
The earth also has seven great areas of land called continents. The map above shows the oceans and continents. Maps usually have a key that shows what a map’s colors and shapes mean.
There are many land and water features on Earth. Land features are called landforms.
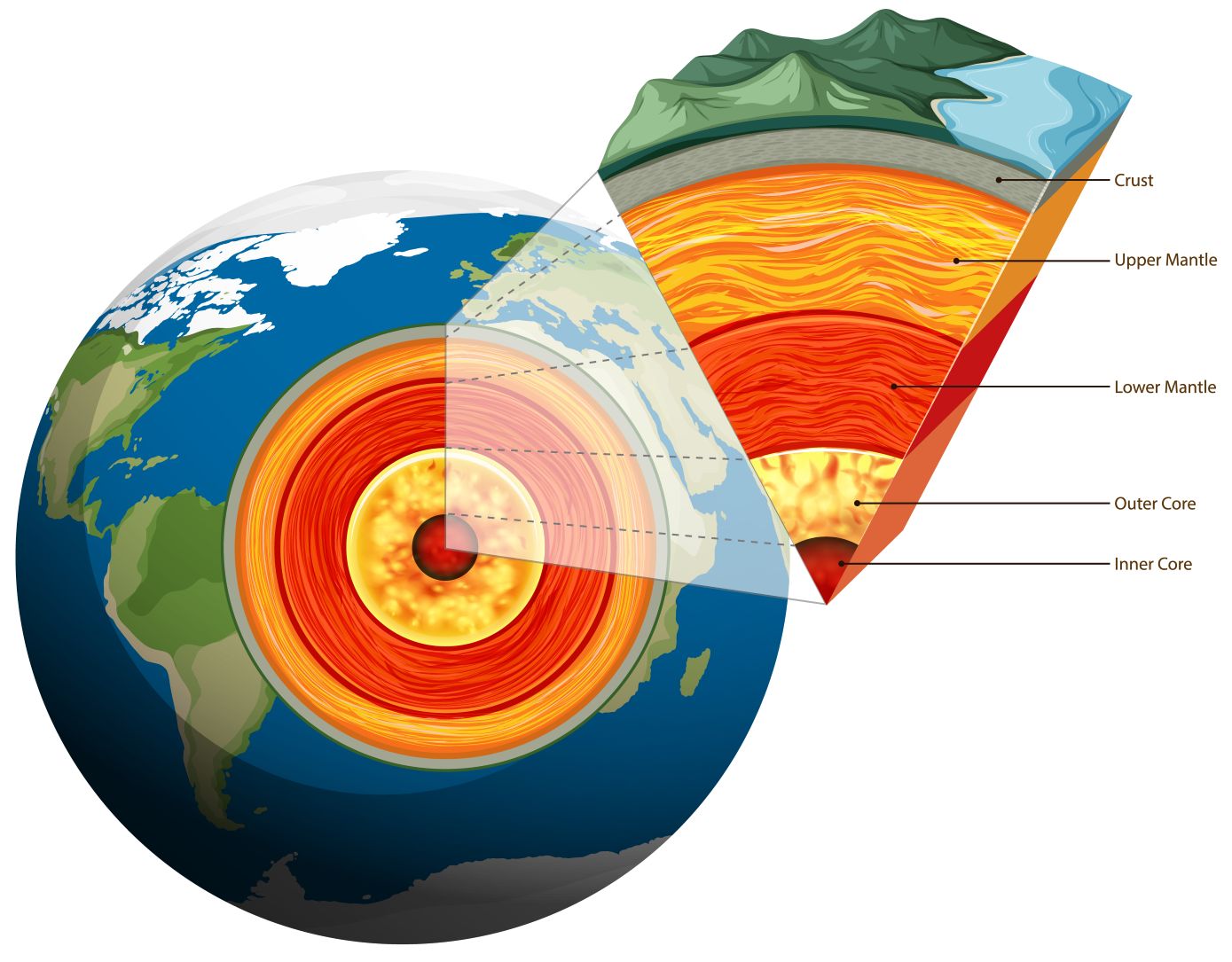
Like an egg, Earth has several layers. The continents and ocean floor make up Earth’s outermost layer, called the crust. The crust is Earth’s thinnest and coolest layer. The layer below the crust is the mantle. Part of the mantle is solid rock. Part is nearly melted rock that is soft and flows. It is a lot like putty. At the center of Earth is the core. The core is the deepest and hottest layer of Earth. The outer core is melted rock. The inner core is solid rock.
The breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces is called weathering. Running water, wind, rain, and temperature changes are some things that break down rocks. Running water and wind pick up small rocks. These rocks scrape against other rocks. This scraping slowly wears away rocks.
Living things can cause weathering. Plants may grow in the cracks of rocks. Their roots eventually split rocks apart. When animals dig in the ground, they can uncover buried rocks. The uncovered rocks can then begin to weather.
Once rocks are weathered, they undergo erosion, that is they are moved to other places. Moving water, wind, and glaciers all cause erosion. A glacier is a mass of ice that moves slowly across the land. Gravity also causes erosion. Gravity can make weathered materials move downhill.


A mineral is a solid, nonliving substance found in nature. Minerals are the building blocks of rocks.
There are more than 3000 kinds of minerals. Each mineral has its own properties.
Properties of Minerals
Color: Most minerals have only one color. A few like Quartz have many colors.
Streak: Streak is the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed across a white tile. A mineral's streak may or may not be the same as the same minerals color.
Luster: This is how light bounces off a mineral. Some minerals are shiny like metal, others are dull.
Hardness: This is a measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. Some minerals are soft and can be scratched with a fingernail. Others are hard and cant even be scratched by a metal.

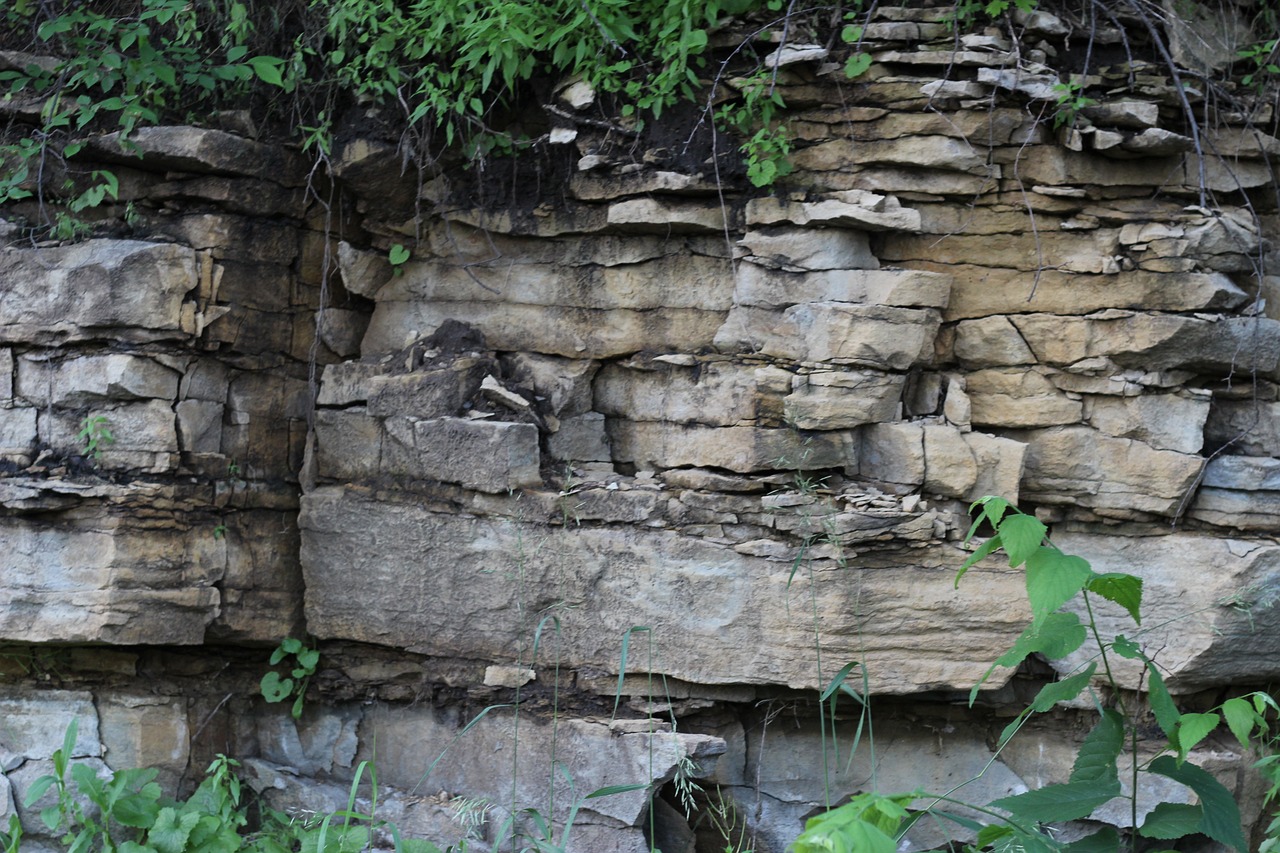
A rock is a non-living material made of one or more minerals. There are several types of rocks. SOme rocks are made of many minerals while others are made predomrinantly by one mineral.
Rocks are made of grains that give the rock its texture. Some rocks have large grains that can be seen easily with just the eyes. Such rocks end up having a rough/coarse texture. Other rocks have fine grains and as a result have a fine/smooth texture.
There are three main kinds of rocks.
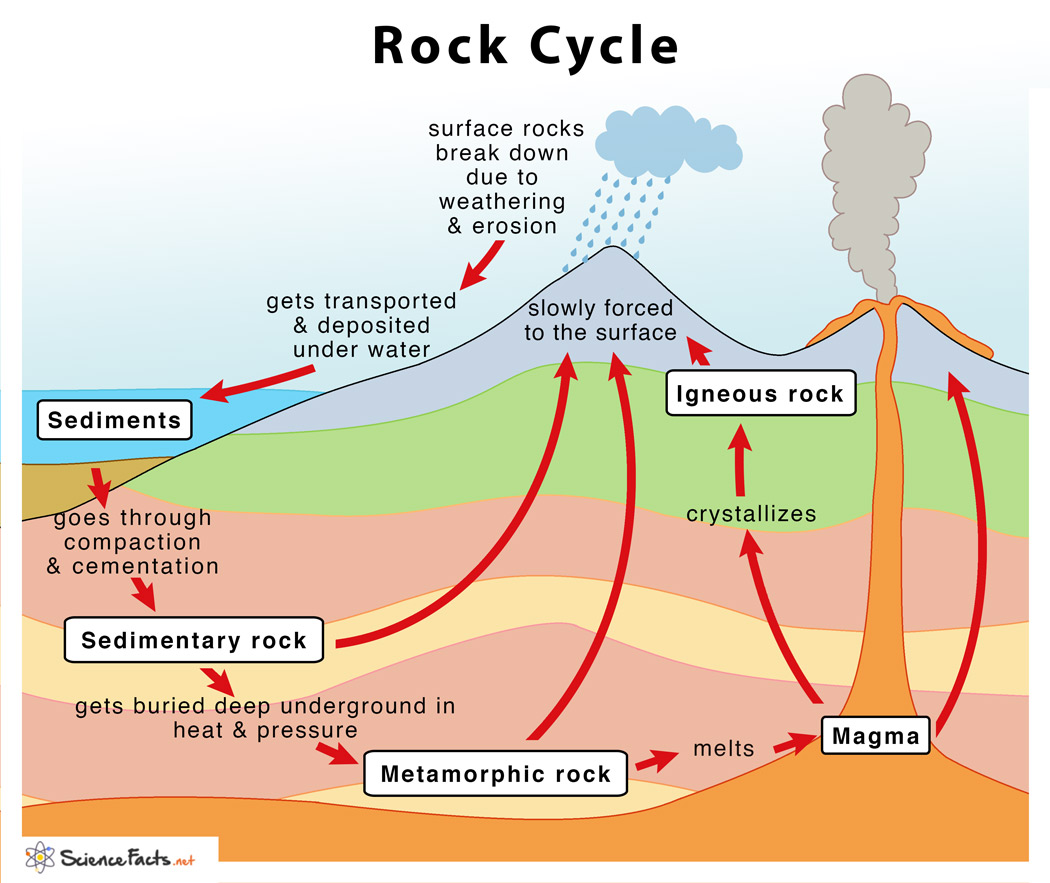
Igneous rocks form when melted rock cools and becomes hard. The molten hot rock inside the earth is called Magma. When this magma flows onto the surface of the earth it is called lava. Lava cools and hardens quickly and results in a rock with smooth grains. When magma cools slowly below the earth surface, it forms granite, which has a corse texture.
Sedimentary rocks form by sediments of weathered rock or fossils. Sandstone, limestone and shale are examples of sedimentary rocks.
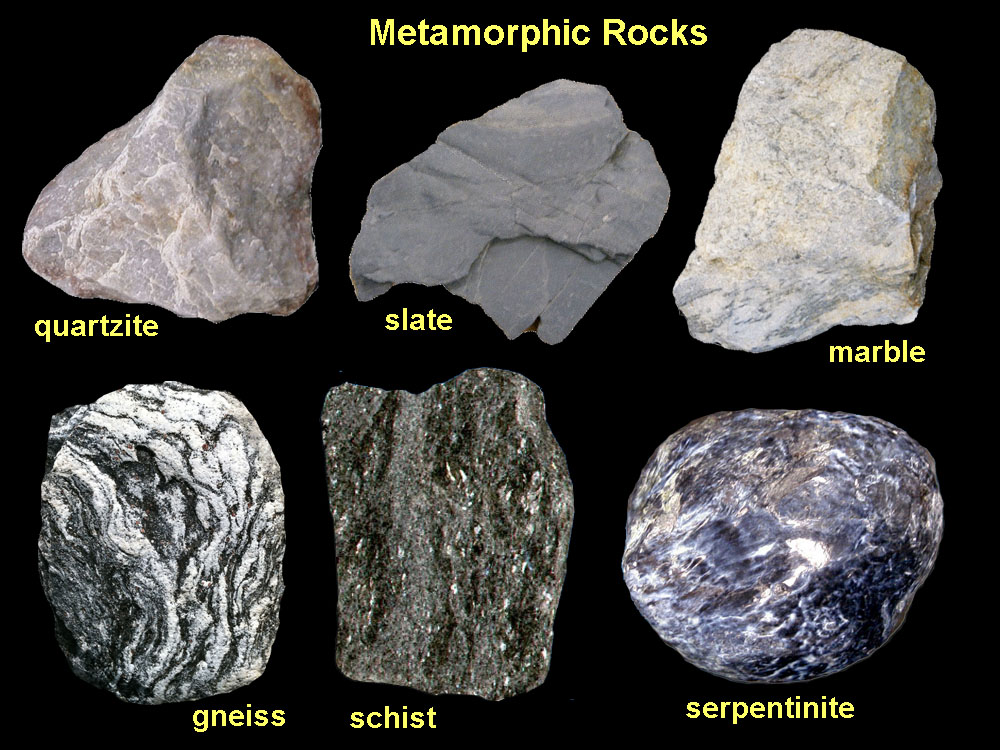
Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have changed by heating and squeezing. Deep inside the earth, the heat and pressure/weight from other rocks creates the heating and squeezing needed to create metamorphic rocks. A new rock forms with properties that are different from the original rock.
Rocks and minerals have multiple uses from building houses, making jewelry and other even more common uses. The mineral graphite is used to make pencil points. Aluminum is used in cooking pans, and electric wires. copper is used in making coins, electric wires and water pipes. Calcium, a mineral which is found in milk, is essential for bone development. It is also predorminant in limestone and may be used to make chalk.



The rock cycle is the process that describes the gradual transformation between the three main types of rocks: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. It is occurring continuously in nature through geologic time.
Steps in the Rock Cycle:
Formation of Igneous Rock – Melting, Cooling, and Crystallization.
Formation of Sedimentary Rock – Weathering, Erosion, Sedimentation, and Compaction.
Formation of Metamorphic Rocks – Metamorphism.
Weathering.
Transportation.
Deposition.
Soil is a mixture of minerals, weathered rocks, and other things. It has bits of decayed plants and animals called humus
Humus is dark in color. It adds nutrients to soil. Plants use these nutrients for their growth. Humus works like a sponge to soak up rainwater and keep the soil moist. Water, air, and living things are also found in soil.
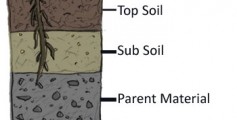
The making of soil starts with weathering. Weathering causes rocks to break down into smaller and smaller pieces. The tiny bits of weathered rock build up into layers.
The top layer is called topsoil. Topsoil is dark and has the most humus and minerals. Below the topsoil is subsoil. This layer is lighter in color and has less humus. Below the subsoil is bedrock, or solid rock.
Soil Color: The color of soil depends on the contents. Soil that has high amount of humus appears dark/black colored. Soil that is high in iron appears red. Soils with high calcite look whitish in color.
Soil Texture: Soil texture is a description of the pieces of grain that make up the soil. Sandy soil has larger grains and does not retain water. Silty soils have smaller grains than sandy soils. Clay soil has the smallest grain sizes. Loam soils is a mixture of sand, silt and clay.

We have already reviewed fossils in our Life Sciences topic.
A fossil fuel is a fuel that forms from the remains of ancient plants and animals.
Oil is a fossil fuel found in rocks deep below Earth’s surface. People use huge drills to dig deep underground for oil. Pumps are used to bring oil to the surface.
Fossil fuels are natural resources. There are two types of natural resources: Renewable and non-renewable resources. Renewable resources are those that can be replaced and used again and again. such as water, animals, plants, air. Non-renewable resources are those that cannot be replaced or reused easily. Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources. Once they are harvested and used, they are lost forever.
Energy can be obtained from renewable resources such as the sunlght (solar energy), wind (wind power), moving water can be used to generate energy.


Position: The location of an object.
Distance: the amount of space between two objects.
Motion: A change in position.
Force: A push or a pull.
Work: The result of a force changing the motion of an object.
Energy: the ability to do work.

An object's position describes the location where the object is. This position is often in relation to another object. for example, the kid is hiding under the table.
The position of an object can also be described based on its distance from another object. The distance between two cars at the parking lot can be about 1 meter.
When an object is changing its position, for example if the boy is moving from the dining room to the bedroom, we can say that the boy is in motion.
Motion can be described in various way, such as upward, downward, straight, zigzag, fast, slow, round, back and forth etc.
The word speed describes how fast the object moves. Therefore, speed determines how much distance an object will move in a specified time. If an object moves faster, it will move a longer distance than an object that is moving slowly.

A force, is simply defined as a push or a pull. Forces can be large or small. Large forces are needed to move heavy objects. The more force you use, the faster the object will move.
There are many types of forces. The forces you are probably most familiar with are contact forces. Contact forces happen between objects that touch. If a soccer player hits a ball, the collision results in contact force. Non-contact forces are those that do not invove contact/collision. A good example is magnetism. Magnets can attract or repel each other. They can also attract things made of certain metals like iron. Magnets can attract or repel objects through solids, liquids, or gases.
Gravity is another example of non-contact forces. Gravity is a pulling force between two objects, such as you and Earth. An object’s weight is a measure of the pull of gravity on it. The more mass an object has, the more gravity pulls on it.
Friction is a force that occurs when one object rubs against another. It pushes against moving objects and causes them to slow down.
People use slippery things such as oil to reduce friction in machines.

In science, work is done when a force moves an object or changes an object's motion. This means that picking up a book from the floor is work.
Work can be easy or hard. Picking up a small pebble is work. Lifting a large stone is work too.
Energy is needed to do work. There are various types of energy:
Kinetic Energy: this is the energy in an object that is in motion. All moving objects such as roller coasters, cars, even people—have kinetic energy.
Potential energy is the kind of energy stored in an object due to its position. If you walk up the steps to the top of a slide, you have high potential energy due to your position at the top of the slide. When you start sliding down the slide, you will convert the potential energy into kinetic energy.
Energy can be transferred from one object to another. If you play bowling and the ball hits the pins and they fall down, energy has been transferred from the ball to the pins.
